NEWS RELEASE October 2019
Determining the Market for Your Product at Every Food Plant
A program to help suppliers of flow and treat products sell to food producers has been introduced by the McIlvaine Company. It predicts the purchases of any product based on the tons of a specific food produced for the next five years. It provides enough technical details and process flow diagrams so that suppliers can craft lowest total cost of ownership (true cost) white papers. A route to the decision makers is also provided. The general program is explained at www.mcilvainecomany.com under Most Profitable Market Program.
Specific forecasts are available for each type of air pollution control, liquid filter or separator, pumps, valves, dryers, heat exchangers, instrumentation, software, steam and electricity generators e.g. for bagasse. Analyses of the potential from each producer also takes into account byproducts or finished products which are manufactured. For sugar this would include alcohol, ethanol and power generation. Here are the major food segments analyzed
Cane sugar is being used as an example. It involves a number of flow and treat processes.
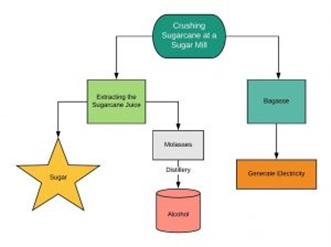
The quantity of crushed cane or bagasse is more than the amount of sugar produced. The bagasse is a good fuel. Sugar mills are combusting it to generate steam for their use and electricity for use and for sale. They are also major producers of alcohol and ethanol. Therefore companies such as Cosan and Tereos, who are major cane sugar producers are bigger prospects than large beet sugar producers in Europe and the U.S.
Flow and treat analyses and forecasts are based on the present and future production in each country and for each significant producer. Here is an example of production forecasts for total sugar production through 2024. We also have these for the cane and beet sugar segments.
|
Sugar Production - 1000 MT |
||||||||||
|
|
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
|
|
Afghanistan |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Albania |
4 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Algeria |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Angola |
40 |
55 |
65 |
60 |
60 |
61 |
63 |
64 |
66 |
|
|
Argentina |
2060 |
2050 |
1870 |
1665 |
1680 |
1726 |
1773 |
1821 |
1871 |
|
|
Armenia |
3 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
The data is also available for the 250 largest sugar producers. We provide profiles and not only sugar production but also co-products such as ethanol.
Sao Martinho
Sao Martinho is a well-established Brazilian company that can trace its roots back as far as 1938. Sao Martinho was initially formed in a series of corporate take overs in which sugar mills were purchased and incorporated into the main corporate structure of Sao Martinho. Prior to 2006, Sao Martinho was known as Companhia Industrial e Agrícola Ometto. Today, Sao Martinho is one of the largest sugar companies in Brazil. Like the other major companies, it does not solely produce sugar, but also produces sugar ethanol as well as other sugar cane products. Sao Martinho currently has two mills dedicated to sugar and sugar ethanol production.
These mills are known as the Iracema Mill and Sao Martinho Mill.
It expects to process 8% more sugarcane in 2019/20 compared with the prior crop year. The company sees its cane crush rising to 22 million tonnes thanks to “better weather conditions and projects aimed at increased productivity, However, the amount of sugar derived from each tonne of cane will fall slightly. Sao Martinho said the total recoverable sugars are expected to be 139 kilograms per tonne, a 2% decrease from the previous season.
Sao Martinho predicted it would produce between 1.055 million to 1.4 million tonnes of sugar and 915 million to 1.1 billion liters of ethanol in the 2019/20 season.
Here are sugar production forecasts for 2019 for some of the companies.
|
Company |
Location |
Production 1000 tons 2018 |
Market share % |
|
COSAN LIMITED |
Brazil |
4,000 (plus ethanol) |
2.1 |
|
Sudzucker |
Germany |
4,800 |
2.5 |
|
Tereos |
France, Brazil |
2900 |
1.5 |
|
Nordzucker |
Denmark, Germany |
2500 |
1.3 |
|
Wilmar |
Australia |
2000 |
1.0 |
|
British Sugar |
UK |
1500 |
0.7 |
|
Mitr Phol |
China |
1300 |
0.6 |
|
American Sugar |
Chalmette LA Refinery |
1,000 |
0.5 |
|
E.I.D.-PARRY (INDIA) LTD. . |
India |
1600 |
0.8 |
|
American Crystal Sugar |
Beet in Upper Mid-west |
1500 |
0.7 |
|
Rogers Sugar Inc. |
Vancouver Only |
240 |
0.1 |
|
Nanning Sugar. |
China |
700 |
0.4 |
We analyze important product developments such as manufacture of cellulosic ethanol.
Raizen completed construction of its first cellulosic ethanol plant where the ethanol will be produced from sugarcane residue. The company invested R$237 million in the plant that will produce 40 million liters of ethanol from sugarcane residue. The plant is located in the city of Piracicaba in the state of Sao Paulo and right next door to one of Raizen's sugar mills that makes sugar and ethanol from sugarcane.
The sugarcane residue from the sugar mill is currently being burned to generate electricity to run the mill with the excess electricity sold back into the electrical grid. The company is now going to divert some of the sugarcane residue to its new facility to produce ethanol. The company feels there are a lot of saving and synergies by placing both plants next door to each other.
Raizen originally estimated that its company-wide ethanol production would increase 50% by producing second generation ethanol. The company had planned to construct seven more cellulose ethanol plants in Brazil by 2024. All of the facilities would be built next door to their existing first generation ethanol plants that use sugarcane. All of the new plants combined could produce up to one billion liters of cellulosic ethanol. However, technical and economic factors have slowed that development. These problems have now been resolved and the company expects cellulosic ethanol to be an important revenue source.
We search for data which will help determine the true cost of a product such as a filter belt or drum filter.
Cordoba belt filters at the Raizen Costa Pinto plant are shown in the YouTube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EZtc_QaR0lw
The following paper is an example of gathering all the evidence. In an effort to compare belt filters with rotary drum filters several areas of interest were investigated over the 2012 and 2013 crops. These included pol losses, bagacillo ratio (bagacillo % feed/mud solids % feed), filter retention (mud in filter cake/mud in feed), filter capacity (filter cake production and removal of mud), belt wash water loss and flocculant usage.
The pol % filter cake average of 3.47. Pol % filter cake from drum filters ranged from 1.00 to 7.36 and averaged 4.08% pol. Belt filters had an average pol % filter cake of 2.36 with a range of 0.46 to 5.86%.
Crop flocculant usage averaged 0.022 lbs./ton cane. Belt filters used a little more flocculant (0.024) on average than drum filters (0.020). On average 5.21 lbs. pol/ton of cane are lost in filter cake for rotary drum filters. Belt filters lost on average 2.71 lbs. pol/ton cane. This included losses in the belt wash water based on a rate of 100 gallons per minute. The overall average filter cake production was 1443 lbs./hr./ft. width. Drum filters averaged 1080 lbs. filter cake and ranged from 128 to 2606 lbs. filter cake/hr./ft. width. Belt filters averaged 2781 lbs./hr./ft. width, almost three times the amount for drums, and ranged from 1509 to 4027 lbs./hr./ft. width.
Regarding belt filters only, the capacity seems to be very high with sugar losses comparable to that of drums. Maintenance costs have yet to be determined. Options for disposal of belt wash water should be considered. https://www.lsuagcenter.com/MCMS/RelatedFiles/%7BBB9E504C-EEAD-4D0C-8249-C67F42F775AA%7D/2014.pdf
A sales program can be constructed with the detailed knowledge of the future purchases at each plant. the best contacts are easily determined through a LinkedIn initiative. Raizen has over 11,400 contacts. But if you want to talk about belt filters at the Costa Pinto plant you can start with the 18 people involved in filtration or the 185 people at the Costa Pinto plant.
|
Raizen LinkedIn Contacts |
|
|
Subject |
# of people |
|
Total on LinkedIn |
11,400 |
|
Centrifuge |
2 |
|
Filtration |
18 |
|
Pumps |
69 |
|
Environment |
1000 |
|
Pollution |
13 |
|
Costa Pinto |
185 |
|
Engineering |
3748 |
|
Vice President |
189 |
|
Cellulosic Ethanol |
22 |
For more information on the flow and treat program for the food industry contact Bob McIlvaine at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. or 847 784 0013 or cell 847 226 2391.



