Global Decisions Positioning System™ (GdPS)
The Global Decisions Positioning System™ (GdPS) is an organized approach to making complex decisions. It has the following elements:
1.) Global Decisions Orchard
2.) Multiple Route Maps
3.) Individual Decision Trees which are continually
Fertilized
Pollinated
1.) The Global Decisions Orchard (GDO)
The GDO consists of multiple Decision Trees with continuing expansion of individual trees and addition of new ones to address the range of business decisions. In order to maximize pollination among the trees there is an Integrated Intelligence System which allows you to locate information in the individual trees. This is shown at:
Decisive Classification of applications, processes, products, contaminants, etc. minimizes confusion. For example, all companies including those in China are identified by a unique number related to the parent corporation. This overcomes a serious problem of multiple name translations.
2.) Multiple Route Maps
The GdPS supplies multiple route maps. Let’s compare it to a GPS system in your car. Assume you could query the “best place to buy a socket wrench from my present location” the ideal GPS would give you routes to the stores starting with the nearest and then the route to the next closest, etc. An enhancement would be a system with the knowledge to show you another route where you would find the cheapest socket wrench and another where you would find the greatest range of socket wrenches. If you are uncertain, it would also be nice to obtain a route to the store or stores with the most helpful sales clerks.
MATS GdPS
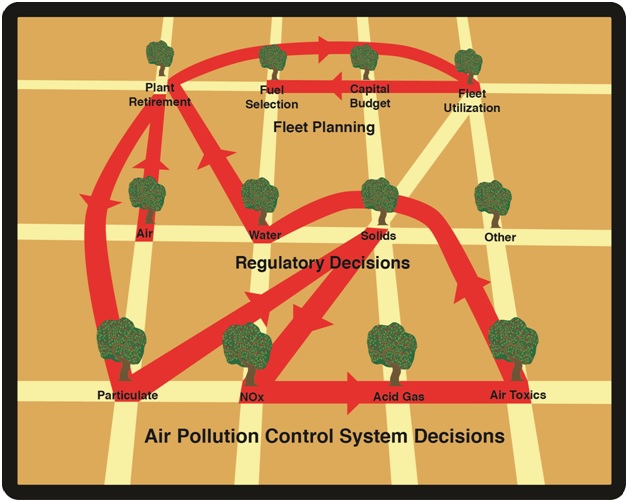
There is a new Air Toxic Rule for U.S. power plants which requires HCl reductions along with some reductions of other pollutants. The above route shows all the Decision Tree Stops needed just to make a decision on how to reduce HCl. If the traveler was more concerned about mercury than HCl, then he would need a slightly different route. The displayed route is for the system purchaser or specifier. The person responsible for approving corrosion materials, electrical controls, or valves would have a different route to follow.
All of these routes will fall into the broader category of a Power Plant Air Quality GdPS. This will be the perspective of the people making the decisions on how to meet the regulations. The plant electrical engineer will have a completely different perspective. He will want to maintain communication ability between the new system controls and existing systems, so he will want to travel a different route.
The GdPS supplies the multiple routes through the Decision Trees. The advantage to the user is as large as the advantage of using the rental car “never lost” system instead an abbreviated map you pick up at the rental car counter.
3.) Individual Decision Trees
The heart of the system is the Orchard of Individual Decision Trees. With decisive classification you have to move from trunk to branch to fruit with the highest level of decision quality as well as ease. Since the factors affecting decisions change continually you need both the fertilization and pollination to insure continuing high quality.
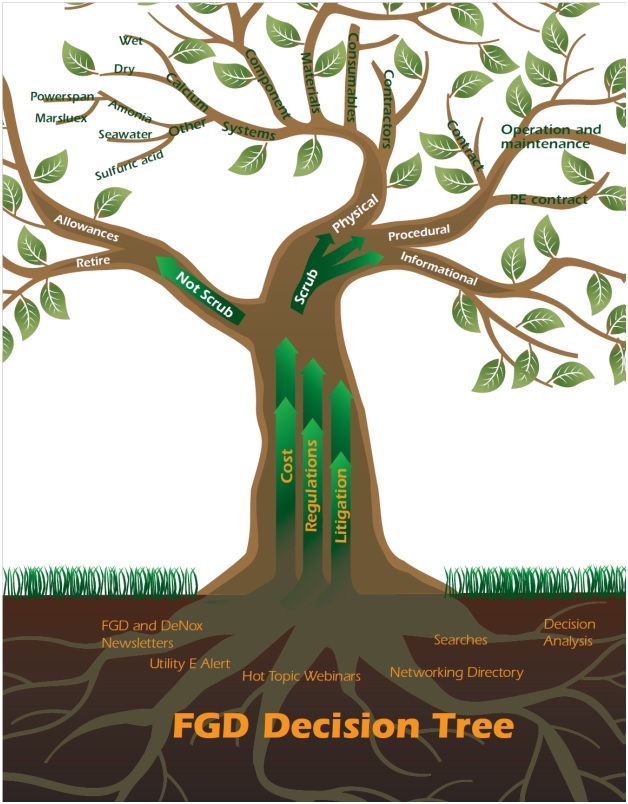
Fertilization: This tree is fertilized by a continuous supply of the 4 Knowledge Needs: Alerts, Answers, Analysis, and Advancement. In this case weekly Alerts and webinars along with intelligence system updates provide powerful fertilizer.
Pollination: Other industries have solutions which need to be considered by the power industry. For example, European waste-to-energy plants are making by-product hydrochloric acid. This technology could be used to advantage at some power plants. The synergistic juxtaposition of Decision Trees in the GDO insures this kind of pollination.
Analysis is greatly enhanced by the creation of templates including a sequence of decisive classifications. Rather than just display a map, the GdPS displays the specific alternative routes whether the goal is speed, minimizing distance or cost. The creation of these routes in many languages is of high importance. The concept is explained at Decisive Classification. Specific examples are shown at: Decisive Classification.
Ten percent of the world’s business knowledge is made inaccessible each year through retirements. Many semi-retired people become consultants. However, there is no mechanism to capitalize on a narrow niche so they become generalists. The GdPS allows them to continue to focus on their niche. Niche Expert System
With the use of Decisive Classification and niche experts the products of any company can be validated using Decisive Validation. An example is shown at Single Use Surgical Apparel.
Most business organizations are hierarchical. The GdPS provides a counter measure to encourage collaboration through the KOC strategy. Individuals if given the knowledge and the right organizational structure will collaborate and perform more effectively with less management. Details of KOC are found at KOC Sales Strategy.
Individuals and businesses make decisions without the benefit of a common metric to measure the potential results. The harm or good of a potential action involves assessment of the risks, application of a tribal value and recognition of the difference in value of a result far into the future than for one which is near term. A system to solve this problem is explained at Sustainability Universal Rating System.



